What is CRM in healthcare?
A CRM (Customer Relationship Manager) is a database of potential and current customers that is combined with automation tools to manage interactions and relationships. Understanding the CRM healthcare definition and its potential to improve care is increasingly essential for modern healthcare providers.
The fundamental purpose of a healthcare CRM is to offer the best patient care throughout the patient journey by empowering staff and supporting providers with simplicity, visibility, and quality. Ultimately, the goal is to improve health and save lives.
A healthcare CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a specialized tool designed to improve patient care, streamline operations, and enhance provider efficiency. Key benefits include:
- Improved patient engagement and satisfaction through personalized care
- Streamlined workflows and reduced administrative burden
- Enhanced care coordination across departments and specialties
- Data-driven insights for better decision-making and resource allocation
- Increased operational efficiency and potential revenue growth
Unlike general CRMs, healthcare CRMs are built to navigate the unique complexities of the healthcare industry, including regulatory compliance, clinical safety, and the intricate patient journey.
What Types of CRM are there?
Sales CRM
 These tools automate emails, outbound calls, and other contact points with prospective or existing customers. The term “CRM” started with sales database and automation tools in the 1970’s that tracked interactions with potential clients. The goal is to keep prospects engaged and move them through defined relationship stages for measurement, predictability, and automation.
These tools automate emails, outbound calls, and other contact points with prospective or existing customers. The term “CRM” started with sales database and automation tools in the 1970’s that tracked interactions with potential clients. The goal is to keep prospects engaged and move them through defined relationship stages for measurement, predictability, and automation.
Marketing CRM
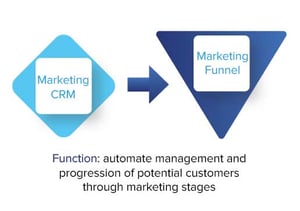 Later, Marketing CRMs brought significant disruption to what had historically been a very creative vertical with data analytics and marketing automation. Marketing CRMs use quantitative analytics to automate advertisements, messaging, email, and content to move prospects through a “funnel.” The goal is to deepen each person's relationship, brand awareness, and trust of the organization. Given the overlap between marketing and sales, these CRMs are now often integrated.
Later, Marketing CRMs brought significant disruption to what had historically been a very creative vertical with data analytics and marketing automation. Marketing CRMs use quantitative analytics to automate advertisements, messaging, email, and content to move prospects through a “funnel.” The goal is to deepen each person's relationship, brand awareness, and trust of the organization. Given the overlap between marketing and sales, these CRMs are now often integrated.
A few dominant sales and marketing CRM companies are Microsoft Dynamics, Salesforce, and Oracle.
Service CRM
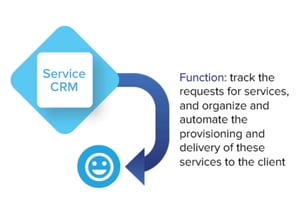 Service CRM tracks and automates the provisioning and delivery of services. These products focus on capturing, documenting and triaging the clients’ needs, then procuring and scheduling resources to address each need.
Service CRM tracks and automates the provisioning and delivery of services. These products focus on capturing, documenting and triaging the clients’ needs, then procuring and scheduling resources to address each need.
These platforms include sophisticated tools such as AI, project management, and big data optimization to smooth specialized workflows. Such service-side automation focuses on managing the workforce and estimating throughput. Most major corporations use a service CRM alongside sales and marketing CRMs.
Names such as BMC Software, ServiceNow, Attlassian, and Zendesk are at the forefront.
What makes a Healthcare CRM
Healthcare CRM is a CRM for the practice of medicine
A specialized CRM in healthcare is crucial for providers looking to improve both patient care and efficiency. including patient acquisition, patient engagement, and care coordination. Cobbling multiple tools together into a digital front door is not enough. The "front door" will lead nowhere unless the delivery of service is optimized and streamlined.
It's crucial to understand that in healthcare, all service is care. Any interaction with patients is an opportunity to deliver care, make them feel valued, and potentially save their life. A healthcare CRM recognizes this and provides tools to ensure every touchpoint is optimized for patient well-being.
Where general CRMs fall short, specialized ones excel. For example, healthcare providers must consider critical factors such as visit history, chronic conditions, insurance provider and current symptoms for the most basic and routine tasks like scheduling and refills.
Providing top-quality patient access to care is a core component of the CRM healthcare meaning. It brings automation to services such as answering patient questions, scheduling appointments, and triaging symptoms over telephone, chat, SMS, or web.
See The Ultimate Guide to improving access, revenues, and outcomes with telehealth
The Purpose of a Healthcare CRM
A healthcare CRM exists to create exceptional care, which in turn leads to exceptional relationships, outcomes, and revenue. It recognizes that a smooth patient experience comes from a smooth staff experience. By supporting and empowering those delivering care, the overall quality of care improves.
A healthcare CRM is designed to make every patient interaction personalized and supportive. As such, the CRM meaning supports healthcare professionals' primary purpose. It focuses on the role of the schedulers, nurses, and contact centers in addressing the following problems:
- Reason for contact
- Understanding the patient context
- Utilizing knowledge management during a conversation
- Checking symptoms by nonclinical agents
- Nurse triage and dispositions
- Matching complicated scheduling requirements
- Managing contact and issue queues
- Refilling prescriptions
- Allocating resources to address patient need quickly
- Delivering health education and information in any format patient needs
- Providing health information in whatever format patient needs
- Conducting telemedicine visits
What are the biggest issues unique to a healthcare CRM?
Clinical care is inherently complex. Keona Health has identified 8 barriers to service that complicates call centers, online service, and overall operations. We call these 8 barriers "Clinical Complexity" and they require that any CRM for healthcare be unique.
Clinical Complexity: A Unique Challenge in Healthcare
One of the most significant issues unique to healthcare CRMs is addressing clinical complexity. This refers to the intricate web of factors that influence patient care and outcomes. Unlike other industries, healthcare must navigate a complex landscape of medical, personal, and systemic variables that can dramatically impact service delivery.
At the heart of this complexity are eight key barriers to optimal care:
- Fragmented Technical Systems: Healthcare often relies on multiple, disconnected IT systems, making it challenging to provide seamless care.
- Regulation & HIPAA Barriers: While crucial for patient privacy, HIPAA regulations can sometimes hinder efficient information sharing and service delivery.
- Patient Health History & Present Symptoms: Each patient's unique medical background and current condition add layers of complexity to decision-making.
- Insurance & Revenue Cycle Management: Navigating various insurance policies and managing the revenue cycle introduces financial complexities to patient care.
- Department & Location Variations: Different healthcare departments or locations may have varying processes and resources, complicating standardized care.
- Provider Preferences: Individual healthcare providers often have unique styles and preferences that need to be accommodated.
- Clinical Safety: Ensuring patient safety, especially in telehealth settings, requires careful consideration and adaptation of existing protocols.
- Fairness & Efficiency: Balancing equitable access to care with equitable provider utilization with the needs of operational efficiency presents ongoing challenges.
A healthcare CRM must be designed to navigate these complexities, providing tools and workflows that simplify decision-making while maintaining high-quality care. By addressing these barriers, a healthcare CRM can help streamline processes, improve patient outcomes, and enhance overall healthcare delivery.
Example of Barriers in Common Healthcare Workflows
For OBGYN practices and most payors, mammogram screening is a key proactive care tool that fills gaps in care and provides an opportunity to check-in with patient overall health and wellbeing.
- When a patient calls in, how do you efficiently identify mammogram-related calls amidst various other inquiries?
- Is there a consistent method across all locations to track scheduling, record data, and verify insurance coverage for mammograms?
- Different locations have varying equipment, capacity, and proximity to patients. How do you optimize throughput while balancing patient convenience and equitable distribution among your resources?
- Can you maintain this quality and consistency when a patient uses alternative communication channels like online chat or a web bot?
- How do you proactively reach patients who are due for mammograms, considering factors like age, risk factors, and previous screening history?
While this example is specific to OBGYN, nearly every specialty faces similar complexities involving all eight barriers to optimal care. For brevity, we'll highlight just a few key challenges for other specialties, but readers should consider how the remaining barriers also apply:
Orthopedics: Joint Replacement Evaluations
- Patient Health History & Present Symptoms: How do you efficiently triage patients who may need joint replacements based on symptoms, imaging results, and conservative treatment history?
- Department & Location Variations: How do you coordinate pre-operative evaluations, surgery scheduling, and post-operative care across multiple departments and locations?
Ophthalmology: Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
- Fragmented Technical Systems: How do you identify and reach out to diabetic patients who are due for retinal screening across different EHR systems?
- Provider Preferences: How do you ensure consistent imaging quality and interpretation across different clinic locations while accommodating individual provider preferences?
Cardiology: Cardiac Stress Tests
- Clinical Safety: How do you prioritize and schedule stress tests based on patient risk factors, symptoms, and urgency?
- Insurance & Revenue Cycle Management: How do you navigate various insurance requirements for cardiac testing authorization and reimbursement?
Neurology: Stroke Prevention Follow-ups
- Fairness & Efficiency: How do you track and schedule regular follow-ups for patients with a history of TIA or minor stroke, ensuring equitable access to care?
- HIPAA Barriers: How do you securely share critical patient information between primary care, neurology, and imaging centers for coordinated stroke prevention care?
These examples highlight just a few of the challenges each specialty faces. Readers are encouraged to consider how the remaining barriers apply in each case, as all eight barriers play a role in the complexity of healthcare delivery across specialties. A comprehensive healthcare CRM must address these multifaceted challenges to truly optimize patient care and operational efficiency.
Dual Focus: Patients and Providers
A unique aspect of healthcare CRMs is their dual focus, embodied in the concepts of Patient 360 and Provider 360. In healthcare, you are providing services to two customers: the patient AND the provider. Delivering quality care to patients means delivering it in a way that supports and serves the provider, enhancing the patient-provider relationship.
Patient 360
A 360-degree view of the patient enables personalized care, improved patient engagement, and more efficient service delivery. Patient 360 offers a comprehensive view of each patient, consolidating their medical history, appointment history, behavior data (calls, texts, etc.), demographics, and other relevant information into a single, accessible platform.
Provider 360
Provider 360 complements this by offering a detailed view of healthcare providers, including their preferences, specialties, scheduling requirements, and performance metrics. This information allows for better resource allocation, improved provider satisfaction, and more effective matching of patients to the right providers.
Patient 360 + Provider 360
When these two 360-degree views are united in a healthcare CRM, the benefits are extraordinary:
- Flawless patient-provider matching, ensuring patients see the most appropriate providers for their needs.
- Improved scheduling accuracy, reducing errors and enhancing both patient and provider satisfaction.
- Optimized patient journey, from initial contact through follow-up care.
- Enhanced marketing capabilities, allowing for targeted, personalized outreach.
- Streamlined operations, including automated waitlisting and rescheduling.
When agents and nurses feel empowered and supported by this comprehensive CRM system, patients feel cared for, and providers trust your team and their competence. This trust is crucial for maintaining high standards of care and ensuring smooth operations across the healthcare organization.
A well-implemented healthcare CRM that unites Patient 360 and Provider 360 helps create a virtuous cycle: it supports staff, who provide better care to patients, which in turn supports providers in their work. This holistic approach is what sets healthcare CRMs apart from other customer relationship management systems, making them indispensable tools for modern healthcare delivery.
What are the features of a healthcare CRM?
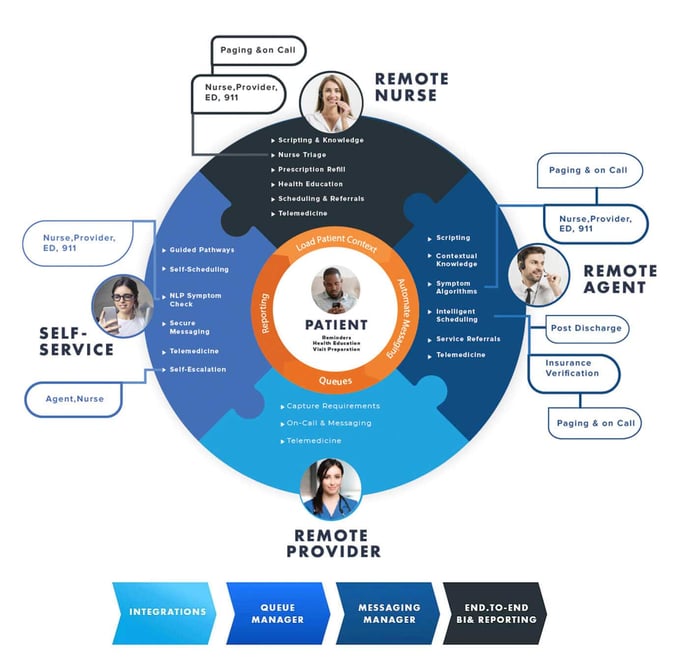
In today's rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, a robust Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is essential for delivering high-quality patient care and maintaining operational efficiency. Based on an advanced maturity model, here are the key features that define a cutting-edge healthcare CRM:
- Standardized Call Management
Modern healthcare CRMs excel at capturing and categorizing call types, enabling standardized handling procedures. This ensures consistent patient experiences and allows for efficient resource allocation. Look for systems that offer customizable call scripts and automated call routing based on type and urgency. - Cross-Departmental Coordination
Top-tier CRMs facilitate seamless service orchestration across departments. They break down silos, improving inter-departmental communication and creating a unified patient journey. Features like shared task lists, automated notifications, and customizable queues (task rules) are crucial for this coordination. - Technology Consolidation
Advanced healthcare CRMs consolidate multiple technologies into a single, comprehensive platform. This integration streamlines operations, reduces IT costs, and enhances data flow. Seek out systems that offer built-in integrations with Electronic Health Records (EHR), billing systems, and other critical healthcare software. - AI-Driven Omnichannel Capabilities
A state-of-the-art healthcare CRM should support omnichannel patient engagement. This includes features for:- Enhanced patient access through multiple channels (phone, email, chat, mobile apps)
- Tools to ensure care continuity across different healthcare settings
- Platforms for consistent and personalized patient education
- Data integration capabilities to support personalized medicine approaches
- Market Expansion and Patient Engagement
Leading CRMs go beyond basic patient management to support growth and engagement. Look for features that aid in:- Patient acquisition through targeted marketing campaigns
- Enhancing patient engagement with personalized communication tools
- Improving care coordination with comprehensive patient histories and care plan tracking
- Advanced Analytics and Real-Time Reporting
Modern healthcare CRMs must offer robust analytics and reporting capabilities to provide actionable insights and support data-driven decision-making. Key aspects include:
- Real-time dashboards: Providing up-to-date statistics on key metrics like average handle time across all healthcare queues.
- Performance coaching: Facilitating comparative analytics for targeted staff coaching and improvement.
- Multi-channel analytics: Offering a holistic view of patient interactions across various communication channels.
- Custom report building: Enabling non-technical users to create tailored reports without IT intervention.
- Revenue forecasting: Utilizing historical data and predictive analytics to project future revenue streams and identify growth opportunities.
- Marketing analysis: Evaluating the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, patient acquisition strategies, and engagement initiatives.
- Operations planning: Supporting resource allocation, staffing decisions, and workflow optimizations based on trend analysis and predictive modeling.
By incorporating these key features, a healthcare CRM can significantly improve patient care, operational efficiency, and organizational growth. As healthcare continues to evolve, CRM systems that align with this maturity model will be crucial in meeting the complex needs of both patients and providers.
|
Ready to assess your organization's healthcare CRM needs? Download our free Healthcare CRM Technology Assessment Checklist |
What is Healthcare Automation and Why is it Critical?
The intricacies of clinical processes often make it challenging for agents to navigate these systems effectively on their own. The 8 barriers of clinical complexity can often result in combinations of well over 1 million possible outcomes to a call. This is where automation becomes crucial, supporting and enhancing key CRM features.
Key automation for healthcare includes:
- Natural Language Symptom Checker: Checking symptoms by non-clincal agents (necessary for healthcare safety):
- Nurse Triage: Triaging patients and providing clinical dispositions by nurses.
- Intelligent Scheduling: Scheduling by business rule and provider requirements:
- Patient self-scheduling: Scheduling directly by patients:
- Referral Service: Referral to specialists or community resources:
- Messaging Manager: Messaging automation to coordinate documentation and service delivery across multiple providers and organizations:
- Knowledge Base: Contact center scripting and knowledge base:
- Overwatch and Business Intelligence: Contact center reporting and management of resources
- Telemedicine: Delivery of Telemedicine
It's crucial to understand that these advanced features are not just nice-to-have additions, but necessities in the face of increasing clinical complexity. Healthcare agents, no matter how well-trained, cannot be expected to manually navigate the intricate web of clinical protocols, patient histories, and regulatory requirements while simultaneously providing high-quality care.
Automation serves as a powerful ally, handling routine tasks, providing decision support, and managing complex workflows behind the scenes. This allows healthcare professionals to focus on what they do best: providing empathetic, personalized care to patients.
By incorporating these key features and leveraging the power of automation, a healthcare CRM can significantly improve patient care, operational efficiency, and organizational growth. As healthcare continues to evolve and increase in complexity, CRM systems that align with this maturity model and embrace automation will be crucial in meeting the intricate needs of both patients and providers.
Example workflow with lots of automation
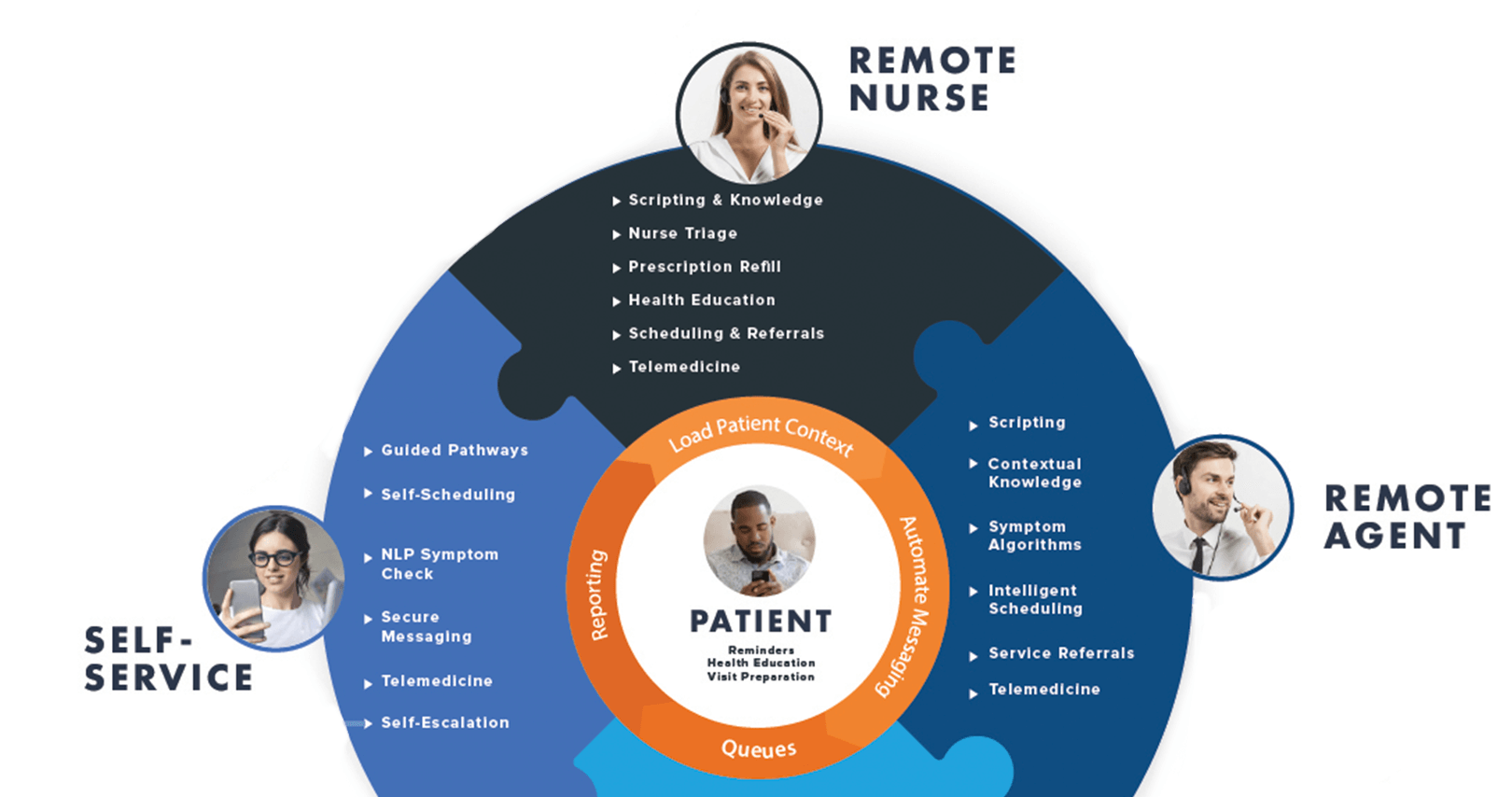
Here is an example of how healthcare CRM automates patient access over the telephone.
When a call comes in, CareDesk pops open and the agent is automatically signed-in. The page is pre-populated with relevant data:
- The EHR is searched based on the patient’s phone number, and relevant matches are ready for the agent to choose
- Knowledge base content loads based on the telephone line called
- Call types are filtered and pre-selected based on the telephone line called and IVR choices made by the caller
- Symptom Checker questions and workflows are automatically filtered based on the patient demographics and location
Each of these bullet points is a step your agents don't have to do!
After pulling in all relevant context from the EHR and other systems, CareDesk provides comprehensive guidance:
- For appointments, Intelligent Scheduling guides the user to the right appointment, using patient’s geo-location, insurance, matching provider preferences, stepping users through even complex multi-resource or multi-visit appointments
- When symptoms are mentioned, agents type whatever patients utter, misspellings are no problem
- Direct agents to the right acuity, indicating what is most appropriate, be that be an appointment, nurse triage, 911, and so on.
- It automatically documents everything in the patient’s chart and appointment as appropriate
- Robust scripting and branching guide the agent through the workflow appropriate to the combination of acuity, patient demographic, location, service line, and time of day
- Provider paging is built-in for specialty triage or after-hours paging
- For nurse triage, it can forward directly to a nurse with pre-loaded triage protocols, care advice, and health information
- For Service Referrals, it takes into account the patient’s geo-location and distance calculations
- Patients can be sent secure messages with pre-visit data and health information specific to their symptoms
This means no more bouncing between 4-8 applications, or following the wrong workflow, or patient requests falling through the cracks. Easily give top-notch experience in one single, guided flow.
Agents aren’t the only ones benefiting from a holistic system. Managers benefit from:
- Ability to customize workflows and content
- Real-time oversight shows summary statistics and activity per queue
- Historical reports present symptom searches and trends
- “Anatomy of an encounter” performance reports facilitate detailed coaching of users, teams, and shifts
- Population trends mapped to zip code
- Business Intelligence tools that allow business users to create reports without the assistance of IT or programmers
Most health care executives don't have access to the metrics that matter. Neither do their managers. With CareDesk, have them at your fingertips at any moment's notice.
By smoothing the path for your agents, CareDesk builds a bridge to provider satisfaction and patient happiness.
Industry Recognition of Healthcare CRMs
As healthcare organizations increasingly recognize the value of specialized CRM solutions, industry analysts are taking note. Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, recently released their 'Market Guide for Healthcare CRM Systems.'
This comprehensive guide analyzes the current landscape of healthcare CRM providers, highlighting key players and trends in the industry.
Keona Health is proud to be recognized in this Market Guide, alongside a select group of healthcare CRM providers. This inclusion underscores our commitment to delivering innovative, healthcare-specific CRM solutions that improve patient care and operational efficiency.
For more resources on a healthcare CRM, see Wikipedia's article here.
How is my existing CRM different?

Many health care organizations use a sales and marketing CRM. As discussed earlier, this is a database that manages the relationship progression of customers along a path or “funnel.” It does this by focusing on the roles of sales, marketing, and care coordination, addressing problems like:
- Identifying opportunities
- Segmenting potential customers
- Communicating your messages based on persona
- Distributing content to customers via multiple channels
- Using analytics to learn which messages work best
- Guiding potential customers through a journey of discovery and choice
- Managing channels and salesforce pipeline
Why are sales and marketing CRMs in healthcare?

Sales and Marketing CRMs are critical to fundraising, community outreach, and partnership management. Because they have tools to automate outbound education and outreach, they are often used to connect with and guide potential donors, referring providers, or partner organizations. They are also helpful in automating patient pathways through services that have pre-defined stages. For example, a sales and marketing CRM might be used for discharge and then move a patient through a care plan, timeline, and offer education.
We have an electronic health record (EHR). This already is a database of patients!

On the surface, an EHR is very similar; it is a database of patients and their medical records. However, its tools and automation are built to facilitate clinicians with:
- Documentation
- Orders
- Prescriptions
- Alerts and tasks
- Chart outcomes
- Meeting regulatory requirements
Most EHRs aren’t designed to help coordinators guide patients through set stages and they they don’t have automation to facilitate non-clinical users or nurses to provide services. Even though some train their users to use the EHR software this way, it is still incredibly clunky and inefficient.
My (EHR/CRM) vendor said they were the only tool we will ever need!

While they may believe this, the truth is that shoehorning healthcare problems into a tool designed for a different purpose is frustrating for users; modifying it is very difficult and expensive. Today, all forward-thinking systems support multiple solutions, integrations, and data exchanges.
CareDesk integrates with an incredible number of systems, including EHRs as well as sales and marketing CRMs (see Integration). It incorporates information into a single contact center flow while also allowing those systems to incorporate Keona Health capabilities into their original workflow.
Why there are so many tools
Different tools, different users
| Software | User |
|---|---|
| Electronic Health Record | for clinicians |
| Practice Management | for billing |
| Sales CRM | for sales |
| Marketing CRM | for marketers |
| Healthcare CRM | for healthcare contact centers |
Software with an intuitive interface streamlines workflow and minimizes clicks. Ironically, the better the software, the clunkier it is when used outside its intended application.
Different users means different automation*
| EHR/PM | S&M CRM | Healthcare CRM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provider, in-person tasks (orders, prescriptions, etc.) |
X | ||
| Automated outreach tasks (patient segmentation, automated outreach, etc.) |
X | ||
| Providers, Nurses, Schedulers, Agents (Telehealth, patient access, triage, scheduling, prescriptions, etc…) | X |
*see detailed table of specific automations above
CareDesk integrates with your existing EHR, PM, CRM, telephone software, communication software and more.
Comparison of automation across types of patient database software
| EHR/PM | S&M CRM | Healthcare CRM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Documentation | X | X | X |
| Orders | X | X | |
| Provider Clinical Decision Support | X | X | |
| Financial Management | X | ||
| Prescriptions | X | X | |
| Alerts and tasks | X | X | X |
| Chart outcomes | X | X | |
| Meeting regulatory requirements | X | HIPAA only | HIPAA only |
| Identifying opportunities | X | ||
| Segmenting potential customers | X | ||
| Communicating your messages based on persona | X | X | |
| Distribute content to patients via multiple channels | X | X | |
| Use analytics to learn which messages work best | X | ||
| Guide potential customers through a journey of discovery and choice | X | ||
| Manage channels and salesforce pipeline | X | ||
| Identification of reason for contact | X | X | |
| Knowledge management during a conversation | X | X | |
| Non-clinical NLP safety check | X | ||
| Nurse triage and dispositions | X | ||
| Matching complicated scheduling requirements | X | ||
| Managing contact and issue queues | X | X | |
| Refilling prescriptions | X | X | |
| Allocating resources to address patient need quickly | X | X | |
| Coordinate multiple resources to address patient need | X | X | |
| Delivering care advice in whatever format patient needs | X | ||
| Providing health information in whatever format patient needs | X | X | |
| Conducting telemedicine visits | X | ||
| Communicate and coordinate with external service partners | X |
Can’t Afford Another CRM

While the cost of implementing a healthcare CRM might seem daunting, consider the value it brings in improving patient care, supporting your staff, and enhancing provider trust. These benefits directly contribute to better health outcomes, which is the ultimate goal of any healthcare organization.
Can you afford to NOT have a Healthcare CRM?
The benefits of a Healthcare CRM have been demonstrated to be substantial, encompassing safety and litigation, revenue optimization, and lower costs:
Litigation:
- Should you be taken to court, you need to have documentation showing proper steps were taken for safety and training, along with what happened during the patient encounter
- A full 50% of telehealth court cases involve actions taken by non-clinical agents, such as schedulers.
- CareDesk provides tools to enhance the patient safety, like Symptom Checker, Triage, and e911.
- CareDesk scripting and guidelines walk users through your processes, so they are less likely to make a mistake
- CareDesk documents every action taken on a telehealth encounter, so you have the data your organization needs to protect itself
Revenue Optimization:
- CareDesk reduces scheduling errors and missed appointments with Intelligent Scheduling
- The waitlist feature automatically fills in lost revenue from cancellations
- Round robin features help fill schedules of new providers
- Patient self-scheduling / re-scheduling allows patients to find appropriate times that match your scheduling rules and notify those in line that a new slot is available
- Mass rescheduling allows you to respond to unanticipated emergencies (like a snowstorm) with minimal loss of revenue
- Steer patients towards the right appointment types, including telemedicine
Lower Costs:
- With a single interface that guides users through every call type, workflow, email, paging, scheduling, while auto-documenting all actions – this lead to:
- Training is drastically cut with a one-page, guided patient interview
- Mistakes, data entry errors, their research and correction are minimized
- Call handle time is reduced by at least 30%, with all integrations implemented
And, most important, it leads to a greater level of care for every patient.
Visit KeonaHealth.com to learn more.
About Keona Health Inc.
Keona develops software to improve communication in the healthcare industry. The flagship product, CareDesk, is a Healthcare CRM and Telehealth platform that provides best care to patients and superior tools for those who serve them.
Posted By

Stephen Dean is COO of Keona Health, where he’s spent 13 years building AI systems that transform patient access. Before “agentic AI” was a term, his team was deploying autonomous systems that now handle millions of patient conversations annually.
Related Post
July 30, 2025
when patients call, they’re not just dialing a number—they’re reaching for help. and...
April 10, 2025
in healthcare, every interaction is a decision point—one that can impact outcomes,...